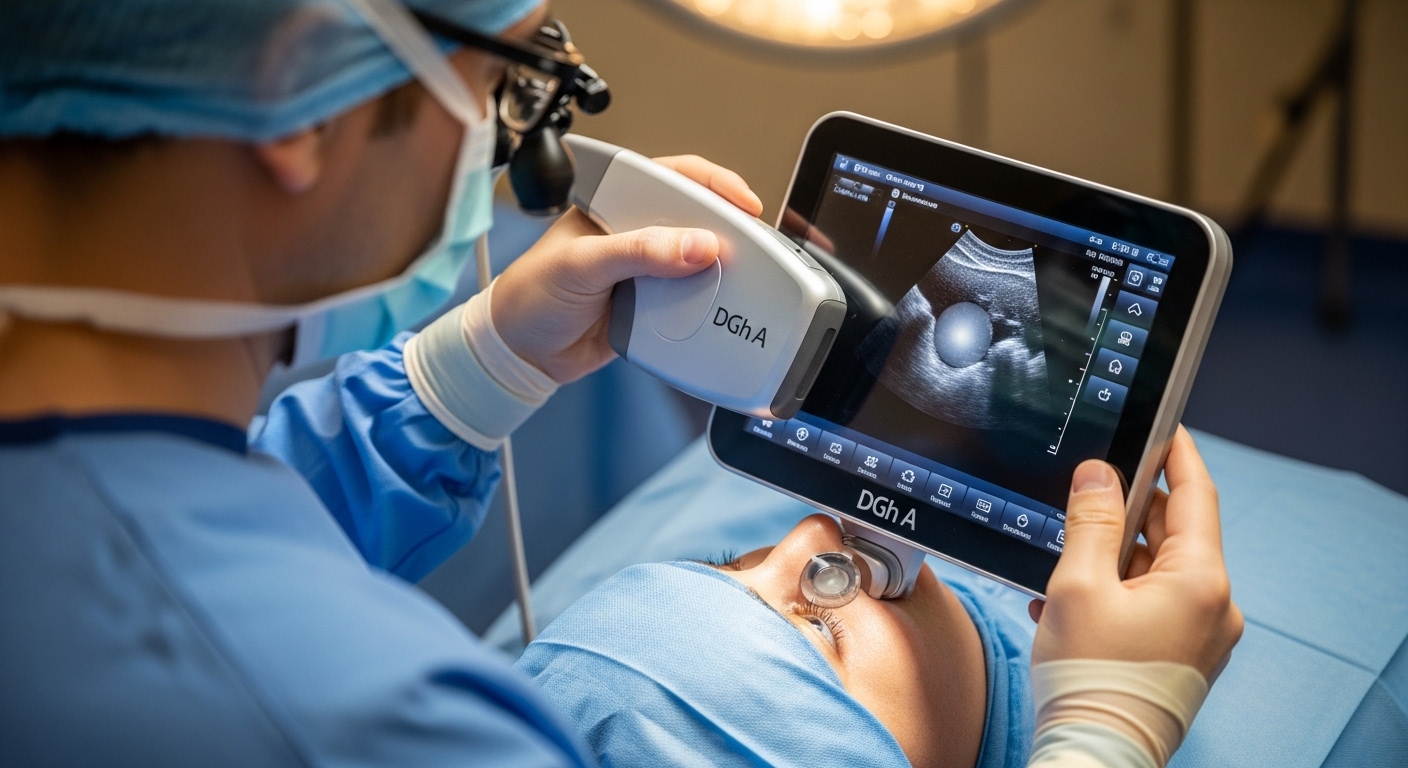
Cataract surgery ranks among the most frequently performed and consistently successful medical procedures worldwide, helping millions regain clear vision annually. DGh A emerges as a groundbreaking portable ultrasound device that transforms how eye care professionals calculate intraocular lens power during surgical procedures. This innovative tool addresses longstanding limitations in traditional measurement approaches that have challenged even experienced ophthalmologists for decades. Understanding its capabilities, clinical results, and future potential helps surgeons and healthcare administrators make informed decisions about adopting this technology.
The Critical Importance of IOL Power Calculation
Why Precision Matters
Every cataract surgeon understands that accurate intraocular lens power determination directly shapes the quality of visual outcomes patients experience after surgery. Even small calculation errors create significant refractive surprises that leave patients requiring glasses or additional corrective procedures afterward. Moreover, imprecise measurements increase patient dissatisfaction, generate negative reviews, and create additional costs for both healthcare providers and patients needing follow-up care. Therefore, investing in technologies that improve measurement accuracy represents a fundamental commitment to delivering excellent surgical outcomes consistently.
Consequences of Calculation Errors
Surgeons who rely on inaccurate measurements risk implanting lenses that leave patients with blurred vision, unwanted astigmatism, or significant residual refractive errors. These outcomes necessitate enhancement procedures like laser vision correction that add expense, recovery time, and emotional stress to patients’ experiences. Additionally, repeated measurement errors damage a surgeon’s professional reputation in communities where patients freely share their surgical experiences with friends and family. Consequently, even highly skilled surgeons recognize that their outcomes depend heavily on the quality of the measurement tools and techniques they employ consistently.
Evolving Patient Expectations
Today’s cataract patients arrive with high expectations shaped by online research, social media testimonials, and premium lens technology marketing campaigns. They expect precise outcomes that minimize or eliminate dependence on corrective eyewear after paying for advanced lens implants. Furthermore, the growing availability of premium toric and multifocal lenses makes accurate measurement even more critical, as these sophisticated implants demand exceptional precision to deliver promised results. Therefore, adopting advanced measurement technology directly addresses the gap between patient expectations and the limitations inherent in older calculation approaches.
Traditional IOL Calculation Methods
Established Formulas and Their Limitations
Surgeons have relied on mathematical formulas including SRK/T, Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, and Barrett Universal II to estimate appropriate lens power from biometry measurements for many years. These formulas perform reasonably well for average eyes but struggle with challenging cases including extremely long or short axial lengths, steep or flat corneas, and post-refractive surgery patients. Moreover, each formula carries systematic biases that produce better results for certain eye types while underperforming for others, requiring surgeons to develop formula selection judgment through years of experience. Additionally, formula-based calculations depend entirely on measurement quality, meaning any inaccuracy in biometry data directly compromises the reliability of subsequent power calculations.
Equipment and Workflow Challenges
Traditional biometry equipment tends toward bulk, expense, and complexity that creates practical challenges for busy surgical practices and outreach programs. Large optical biometry units require dedicated clinic space, reliable power sources, and significant capital investment that strains smaller practice budgets. Furthermore, transporting traditional equipment to remote locations, satellite clinics, or patients with limited mobility proves impractical or completely impossible in many real-world scenarios. Similarly, staff training requirements for complex traditional systems consume time and resources that practices could otherwise direct toward patient care and service expansion.
Manual Process Vulnerabilities
Human error introduces variability into traditional measurement processes despite the best efforts of trained and experienced technicians performing routine measurements. Manual data entry transfers measurement values from equipment to formula calculators, creating opportunities for transcription errors that affect final lens power selections. Moreover, patient cooperation challenges, corneal irregularities, and media opacities can compromise measurement quality in ways that aren’t always immediately apparent to technicians performing the assessments. Consequently, these accumulated vulnerabilities in traditional approaches create compelling motivation for adopting streamlined technologies that reduce process complexity and associated error opportunities.
Introducing the DGh A Device
Core Technology and Design Philosophy
Engineers designed the DGh A portable ultrasound device specifically to address the portability, accuracy, and usability limitations that characterize traditional biometry approaches in clinical settings. The device combines advanced ultrasound imaging capabilities with an intuitive user interface housed within a compact, lightweight form factor that professionals can transport effortlessly between locations. Moreover, the design prioritizes clinical workflow efficiency, allowing surgeons and technicians to complete accurate measurements without the elaborate setup procedures that traditional equipment requires before each use. This thoughtful engineering approach reflects deep understanding of real-world surgical practice needs rather than simply transferring laboratory technology into clinical environments.
Portability and Accessibility Advantages
The compact dimensions and lightweight construction allow clinicians to carry the device easily between examination rooms, surgical facilities, hospital wards, and remote outreach locations. Surgeons can perform bedside assessments for patients with limited mobility, eliminating transportation challenges that previously delayed or prevented timely cataract surgery for vulnerable populations. Additionally, battery operation frees the device from dependence on wall power, enabling use in locations where electrical infrastructure proves unreliable or unavailable for extended periods. Furthermore, this portability democratizes access to high-quality biometry, allowing surgeons in resource-limited settings to achieve measurement accuracy previously available only in well-equipped urban facilities.
User Interface and Learning Curve
The device features an intuitive interface that experienced professionals and relative newcomers alike can master quickly without extensive formal training programs. Clear on-screen guidance walks users through measurement procedures systematically, reducing reliance on memorized protocols that vary between experienced staff members. Moreover, consistent interface design across measurement types helps users build confidence rapidly, which translates directly into smoother workflow integration during busy clinical days. Consequently, practices can deploy the device broadly across their teams without incurring the substantial training costs and productivity losses that accompany the introduction of more complex traditional systems.
Key Features and Technical Capabilities
Advanced Imaging Technology
The device incorporates sophisticated ultrasound imaging technology that produces high-resolution measurements essential for accurate lens power determinations across diverse patient populations. Signal processing algorithms filter noise and artifacts that might otherwise compromise measurement reliability in challenging eyes with dense cataracts or irregular internal structures. Furthermore, multiple measurement averaging capabilities automatically identify and reject outlier readings that might indicate measurement artifacts rather than true anatomical dimensions. This intelligent data processing reduces operator-dependent variability, ensuring consistent results regardless of which trained staff member performs patient assessments throughout the day.
Battery Performance and Durability
Extended battery life allows clinicians to complete full surgical lists or outreach clinic sessions without interruption for recharging, supporting seamless operational workflows. The device withstands the physical demands of regular clinical use including transport between locations, multiple daily measurements, and the inevitable minor impacts that occur in busy healthcare environments. Moreover, durable construction minimizes maintenance requirements and repair costs that can significantly affect total cost of ownership calculations over typical equipment lifecycles. Additionally, the combination of durability and portability makes the device particularly valuable for humanitarian eye care missions where reliable equipment performance in challenging conditions proves absolutely essential.
Wireless Connectivity and Data Management
Wireless capabilities enable seamless data transfer between the device and electronic health record systems, eliminating manual data entry that introduces transcription errors. Measurement results flow automatically into patient records, formula calculation software, and surgical planning systems that surgeons use to finalize lens power selections. Furthermore, digital data storage preserves complete measurement histories that support outcomes analysis, quality improvement initiatives, and medico-legal documentation requirements for all patients. This connectivity transforms the device from a standalone measurement tool into an integrated component of the broader digital healthcare ecosystem that modern surgical practices require.
Measurement Precision Standards
Clinical validation demonstrates that the device achieves measurement precision comparable to larger, more expensive traditional systems while offering significant practical advantages in portability and ease of use. Axial length measurements show excellent repeatability across consecutive readings, confirming that the device delivers reliable data rather than highly variable results that undermine clinical confidence. Moreover, corneal measurement capabilities provide the curvature data that lens power formulas require, completing the biometry dataset within a single compact device rather than requiring multiple separate instruments. Therefore, clinicians gain comprehensive measurement capabilities without sacrificing the portability advantages that distinguish this device from conventional alternatives.
Clinical Study Results
Success Rate Data
Rigorous clinical studies evaluating the device across diverse patient populations demonstrate consistently impressive results that validate its clinical utility in real surgical practice settings. Studies report target refraction achievement rates exceeding ninety percent, matching or surpassing outcomes traditionally associated with premium optical biometry systems costing considerably more. Moreover, refractive surprise rates decrease significantly when surgeons transition from traditional measurement approaches to this device, directly translating into improved patient satisfaction scores after surgery. Consequently, these outcome improvements justify adoption decisions both clinically and financially for practices prioritizing excellent surgical results.
Surgeon Satisfaction and Feedback
Ophthalmologists who integrated the device into their practices report high satisfaction with its performance, particularly praising the combination of measurement accuracy and workflow efficiency improvements. Many surgeons note that the device’s portability enables same-day biometry and surgical planning in outpatient settings where traditional equipment logistics previously caused scheduling complications. Additionally, surgeons appreciate reduced measurement failures in challenging cases including dense cataracts, where ultrasound-based approaches succeed when optical methods struggle to obtain reliable readings. Furthermore, positive experiences shared through professional networks accelerate adoption among colleagues who trust peer recommendations over manufacturer marketing materials.
Patient Outcome Improvements
Patients benefit directly from the improved measurement accuracy that the device delivers, experiencing better uncorrected visual acuity after surgery than comparable patients measured with traditional approaches. Reduced rates of additional corrective procedures following primary cataract surgery represent meaningful improvements in patient experience and healthcare resource utilization across practice populations. Moreover, faster measurement processes reduce patient chair time and appointment anxiety, contributing to the overall positive experience that drives high satisfaction scores and referral recommendations. These patient-centered outcome improvements ultimately represent the most compelling argument for surgical practices considering investment in this technology.
Cost Analysis and Financial Considerations
Acquisition Cost Comparison
The device carries a significantly lower purchase price than premium optical biometry systems, reducing the capital investment barrier that prevents smaller practices from accessing advanced measurement technology. Lower upfront costs accelerate return on investment timelines, making financial approval easier for practice administrators evaluating technology acquisition proposals. Moreover, reduced maintenance requirements and minimal consumable costs keep ongoing operational expenses low throughout the device’s useful clinical life. Additionally, practices operating multiple locations can equip each site with dedicated devices without the budget constraints that force single expensive equipment units to travel between facilities inconveniently.
Operational Efficiency Gains
Faster measurement procedures allow practices to increase patient throughput without extending clinic hours or hiring additional staff to manage growing surgical volumes. Reduced training time for new staff members translates into quicker deployment and lower onboarding costs compared to complex traditional systems requiring extensive competency development. Furthermore, eliminated manual data entry saves measurable staff time daily, reducing labor costs while simultaneously improving data accuracy by removing transcription error opportunities. Consequently, these operational efficiency improvements generate ongoing financial benefits that accumulate substantially over multi-year periods following initial device acquisition.
Revenue Enhancement Opportunities
Improved surgical outcomes reduce the rate of enhancement procedures that practices perform at no additional charge due to measurement-related refractive surprises. Practices offering convenient same-day consultation and measurement services attract patients who value efficiency, potentially increasing surgical volumes from competitors offering less convenient workflows. Moreover, capabilities for outreach programs and remote clinic services expand the geographic catchment area from which practices draw surgical patients, supporting revenue growth beyond traditional service boundaries. Therefore, the financial case for adoption extends beyond simple cost reduction to encompass genuine revenue enhancement opportunities that strengthen practice financial performance.
Impact on Surgical Practices
Workflow Integration
Successful integration requires thoughtful planning around how the device fits into existing patient flow, staff responsibilities, and surgical planning processes within each specific practice environment. Training programs should emphasize not just device operation but also how measurement data flows into formula calculators, electronic records, and surgical planning discussions between technicians and surgeons. Additionally, establishing clear protocols for challenging cases where multiple measurement approaches might be appropriate ensures consistent decision-making across different staff members and patient presentations. Furthermore, regular outcome audits help practices identify whether device integration delivers expected improvements and highlight opportunities for further workflow refinement over time.
Expanding Surgical Reach
The portability advantage fundamentally changes which patients practices can serve efficiently, opening opportunities to provide surgical care to populations previously underserved due to geographic or mobility barriers. Mobile surgical programs, nursing home visits, and rural outreach clinics become more viable when surgeons can perform quality preoperative biometry outside traditional clinic settings. Moreover, the ability to assess patients at satellite locations without transporting expensive fragile equipment reduces logistical complexity that previously discouraged practices from establishing outreach programs. Consequently, practices adopting this approach can grow their surgical volumes while fulfilling meaningful community service missions that enhance professional satisfaction and organizational reputation.
Training Program Evolution
Ophthalmology residency and fellowship training programs increasingly incorporate advanced biometry technology into their curricula, reflecting the growing clinical importance of measurement quality in surgical outcomes. Trainees learning on devices that match real-world practice equipment develop directly applicable skills rather than theoretical knowledge requiring translation to different equipment in their future practices. Furthermore, simulation and supervised practice opportunities with portable devices prepare residents for the full range of clinical settings they’ll encounter throughout their careers, including outreach and resource-limited environments. This educational evolution ensures the next generation of cataract surgeons enters practice fully prepared to leverage modern measurement technology effectively from the start of their independent careers.
Future Technology Developments
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Researchers actively develop AI integration capabilities that will enable the device to analyze measurement data and generate optimized lens power recommendations automatically based on vast outcome databases. Machine learning algorithms trained on millions of surgical cases can identify subtle measurement patterns associated with superior outcomes, surpassing the pattern recognition capabilities of even highly experienced individual surgeons. Moreover, AI assistance will prove particularly valuable for challenging cases where traditional formula selection involves significant uncertainty and where outcome prediction currently relies heavily on surgeon experience and judgment. Therefore, AI integration represents a transformative enhancement that will dramatically expand the clinical utility of portable ultrasound measurement technology in challenging patient populations.
Enhanced Imaging Capabilities
Ongoing engineering development focuses on improving ultrasound frequency, resolution, and signal processing algorithms that will further enhance measurement precision beyond already impressive current performance levels. Next-generation sensors will provide clearer visualization of internal eye structures, improving measurement accuracy particularly in eyes with irregular anatomy, previous surgical changes, or advanced lens opacification that challenges current technology. Additionally, three-dimensional measurement capabilities under development will capture ocular dimensions that current two-dimensional approaches miss, potentially enabling entirely new approaches to lens power calculation and selection. Furthermore, these imaging improvements will expand the range of challenging cases where portable ultrasound succeeds, reducing measurement failures that currently require alternative assessment approaches.
Connectivity and Platform Expansion
Future versions will offer deeper integration with surgical planning platforms, electronic health records, and telemedicine systems that collectively form the digital infrastructure of modern ophthalmic surgical practice. Cloud-based data sharing will enable real-time consultation between surgeons at different locations, facilitating collaborative case planning for complex patients who benefit from multiple expert perspectives. Moreover, integration with outcome tracking platforms will create continuous feedback loops where measurement data links to surgical results, enabling ongoing refinement of lens selection strategies based on real-world performance data. Consequently, the device will evolve from a measurement instrument into an intelligent platform component that contributes to continuous quality improvement across the surgical practices that adopt it.
Global Accessibility Goals
Manufacturers recognize enormous unmet need for quality cataract surgery in developing regions where billions of people suffer preventable vision loss due to inadequate surgical infrastructure and equipment access. Future device development prioritizes further cost reduction and durability improvements that will make the technology accessible in the lowest-resource settings where surgical intervention can most dramatically transform individual lives and community productivity. Additionally, simplified training programs and multilingual interfaces will enable deployment in settings where formal ophthalmology training infrastructure remains limited or underdeveloped. Moreover, partnerships with global health organizations will facilitate technology distribution programs that accelerate access beyond what commercial market forces alone would achieve through conventional channels.
Conclusion
The DGh A portable ultrasound device represents a meaningful advancement in cataract surgery technology that addresses real limitations affecting surgical outcomes and practice efficiency worldwide. Its combination of measurement accuracy, genuine portability, intuitive operation, and favorable economics creates a compelling value proposition for surgical practices of all sizes and resource levels. Moreover, clinical study results demonstrating exceptional target refraction achievement rates validate the technology’s performance claims with rigorous evidence rather than marketing assertions alone. As artificial intelligence integration, enhanced imaging, and expanded connectivity capabilities emerge in future iterations, this technology’s clinical impact will grow substantially beyond already impressive current performance. Practices that embrace this innovation position themselves to deliver superior patient outcomes, serve broader populations, and operate more efficiently in an increasingly competitive and demanding surgical care environment.