Introduction
Modern communication systems require sophisticated technology to connect multiple participants across different locations simultaneously. Therefore, the multipoint control unit serves as the backbone of contemporary videoconferencing infrastructure. Furthermore, this critical component enables organizations to conduct seamless meetings with participants from various geographical locations worldwide.
Initially, businesses relied on simple point-to-point connections for remote communication, which limited their collaborative capabilities significantly. However, technological advancement has transformed how organizations approach remote meetings and collaborative work environments today. Consequently, understanding these systems becomes essential for IT professionals implementing modern communication solutions.
What Is a Multipoint Control Unit?
Definition and Core Purpose
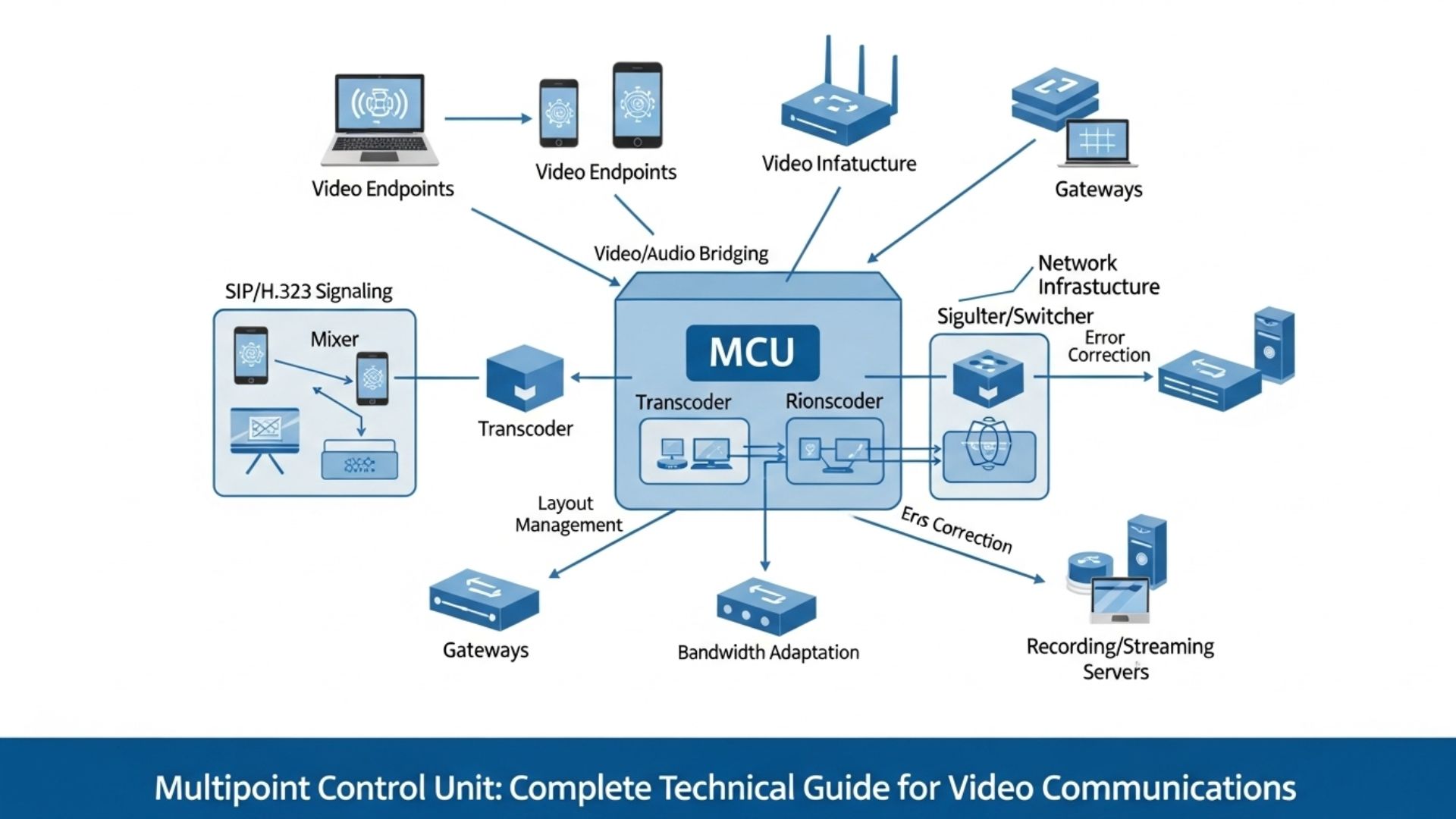
A multipoint control unit represents a specialized hardware or software system that manages multiple simultaneous communication streams effectively. Moreover, this system coordinates audio, video, and data transmission between various endpoints during collaborative sessions. Additionally, it serves as the central hub that processes and distributes multimedia content to all connected participants.
Organizations deploy these systems to facilitate large-scale meetings involving participants from multiple locations across different time zones. Furthermore, the system ensures consistent quality and synchronization across all connected endpoints throughout the entire communication session. Therefore, businesses can maintain professional standards while conducting critical meetings with remote teams and external stakeholders.
Primary Functions and Capabilities
These systems perform several critical functions that enable successful multi-party communication sessions across various network environments. First, they aggregate incoming audio and video streams from multiple participants into coherent, manageable data flows. Additionally, they process and optimize multimedia content to ensure optimal quality delivery to all connected endpoints.
Subsequently, the system distributes processed content to appropriate recipients based on predefined conference parameters and participant requirements. Furthermore, it manages bandwidth allocation dynamically to maintain consistent quality levels throughout the entire communication session. Therefore, participants experience smooth, uninterrupted communication regardless of their location or network conditions.
Read More: iRobux Login: Your Gateway to Enhanced Gaming Experience
Technical Architecture and Components
Core System Architecture
The fundamental architecture consists of several interconnected components that work together to deliver comprehensive communication capabilities. Initially, the system receives multiple input streams from various endpoints through different network protocols and connection types. Then, it processes these streams using specialized hardware or software algorithms to optimize quality and performance.
Moreover, the central processing unit coordinates all system operations while managing resource allocation and performance optimization continuously. Additionally, dedicated modules handle specific functions such as audio mixing, video switching, and protocol translation between different systems. Consequently, the entire system operates as a cohesive unit that delivers seamless communication experiences.
Hardware Components
Physical implementations typically include powerful processing units capable of handling multiple high-definition video streams simultaneously without performance degradation. Furthermore, these systems incorporate specialized audio processing chips that manage complex mixing operations for multiple participants. Additionally, network interface cards provide high-bandwidth connections to accommodate various communication protocols and data transmission requirements.
Memory subsystems play crucial roles in buffering and processing multimedia content while maintaining synchronization across all streams. Moreover, dedicated graphics processing units accelerate video encoding and decoding operations to ensure optimal performance levels. Therefore, hardware specifications directly impact system capacity and overall performance capabilities in demanding environments.
Software Components
Software implementations leverage advanced algorithms and protocols to manage communication sessions efficiently across diverse network environments. Initially, the control software manages session establishment, participant authentication, and resource allocation based on predefined policies. Furthermore, signal processing modules handle audio and video optimization, ensuring consistent quality across all connected endpoints.
Additionally, protocol translation modules enable interoperability between different communication systems and standards used by various organizations. Moreover, management interfaces provide administrators with comprehensive control over system operations, monitoring capabilities, and configuration options. Consequently, software components determine system flexibility, scalability, and integration capabilities with existing infrastructure.
Communication Protocols and Standards
H.323 Protocol Suite
The H.323 standard represents one of the most widely adopted protocols for multimedia communication systems worldwide. Initially, this protocol suite defines comprehensive specifications for audio, video, and data transmission over packet-switched networks. Furthermore, it establishes standardized procedures for call setup, media negotiation, and session management between different systems.
Additionally, H.323 incorporates various codecs and compression algorithms that optimize bandwidth utilization while maintaining acceptable quality levels. Moreover, the protocol includes security mechanisms and authentication procedures to protect sensitive communication content from unauthorized access. Therefore, organizations can implement secure, reliable communication systems that comply with international standards.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
SIP represents a modern, flexible protocol that simplifies session establishment and management for multimedia communication applications. Moreover, this protocol uses text-based messages that facilitate easy integration with existing network infrastructure and management systems. Additionally, SIP supports dynamic participant addition and removal during active communication sessions.
Furthermore, the protocol enables advanced features such as call forwarding, conferencing, and presence management across distributed communication environments. Subsequently, organizations can implement sophisticated communication workflows that enhance productivity and collaboration capabilities significantly. Therefore, SIP adoption continues growing among organizations seeking modern, scalable communication solutions.
Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP)
RTP provides essential mechanisms for delivering real-time multimedia content across network infrastructures with varying quality characteristics. Initially, this protocol manages timestamp synchronization and sequence numbering to ensure proper media stream reconstruction at endpoints. Furthermore, it incorporates quality monitoring and adaptive mechanisms that respond to changing network conditions automatically.
Additionally, RTP works closely with companion protocols to provide comprehensive quality of service management for multimedia applications. Moreover, the protocol supports various payload formats and encoding schemes that accommodate different media types and quality requirements. Consequently, organizations can maintain consistent communication quality across diverse network environments and connection types.
Types and Configurations
Centralized Architecture
Centralized configurations concentrate all processing and control functions within a single, powerful system that manages entire communication sessions. Initially, all participants connect directly to the central unit, which processes and redistributes multimedia content accordingly. Furthermore, this approach simplifies management and provides centralized control over all communication parameters and quality settings.
Additionally, centralized systems offer excellent scalability options for organizations with growing communication requirements and expanding participant numbers. Moreover, administrators can implement comprehensive security policies and access controls from a single management interface effectively. Therefore, centralized architectures suit organizations requiring strict control and standardized communication experiences across all sessions.
Distributed Architecture
Distributed configurations spread processing and control functions across multiple interconnected nodes that collaborate to deliver communication services. Furthermore, this approach improves system resilience by eliminating single points of failure that could disrupt entire communication sessions. Additionally, distributed systems can provide better performance by processing multimedia content closer to endpoint locations.
Moreover, this architecture enables organizations to implement geographically distributed communication networks that serve global operations effectively. Subsequently, participants experience reduced latency and improved quality when connecting to nearby processing nodes rather than distant centers. Therefore, distributed architectures benefit organizations with global operations requiring consistent, high-quality communication capabilities.
Hybrid Implementations
Hybrid systems combine centralized and distributed elements to optimize performance, scalability, and management capabilities according to specific requirements. Initially, organizations can deploy centralized control functions while distributing processing capabilities across multiple locations strategically. Furthermore, this approach provides flexibility in adapting to changing requirements and scaling operations efficiently.
Additionally, hybrid implementations enable organizations to optimize costs by deploying processing capacity where needed most while maintaining centralized management. Moreover, these systems can adapt to varying traffic patterns and participant distributions dynamically throughout different periods. Consequently, hybrid architectures offer optimal balance between performance, cost, and management complexity for diverse organizational needs.
Key Features and Capabilities
Audio Processing and Mixing
Advanced audio processing capabilities ensure clear, intelligible communication by managing multiple simultaneous speaker inputs and background noise. Initially, the system applies noise reduction algorithms that filter unwanted sounds while preserving speech quality and clarity. Furthermore, automatic gain control maintains consistent volume levels across all participants regardless of their microphone characteristics.
Additionally, echo cancellation algorithms prevent audio feedback loops that could disrupt communication sessions and participant experience. Moreover, the system provides intelligent mixing capabilities that highlight active speakers while managing background conversations appropriately. Therefore, participants enjoy natural, clear audio quality that facilitates effective communication and collaboration.
Video Management and Distribution
Sophisticated video processing capabilities handle multiple high-definition streams while optimizing bandwidth utilization and maintaining visual quality standards. Initially, the system performs real-time video encoding and decoding operations to accommodate various endpoint capabilities and network conditions. Furthermore, intelligent switching algorithms determine optimal video layouts and speaker selection based on participant activity.
Additionally, the system supports various video resolutions and frame rates to accommodate different endpoint capabilities and bandwidth constraints. Moreover, advanced scaling algorithms ensure optimal video quality delivery regardless of participant device characteristics or network conditions. Consequently, all participants receive appropriate video quality that enhances their communication experience and engagement levels.
Bandwidth Management
Dynamic bandwidth management ensures optimal resource utilization while maintaining acceptable quality levels for all session participants simultaneously. Initially, the system monitors network conditions continuously and adjusts encoding parameters to prevent congestion and quality degradation. Furthermore, intelligent prioritization algorithms allocate bandwidth based on content importance and participant requirements.
Additionally, adaptive mechanisms respond to changing network conditions by adjusting quality parameters and resource allocation automatically. Moreover, the system provides administrators with comprehensive bandwidth monitoring and control capabilities for proactive management. Therefore, organizations can optimize network resource utilization while ensuring consistent communication quality across all sessions.
Implementation Strategies
Planning and Requirements Analysis
Successful implementation begins with comprehensive analysis of organizational communication requirements, existing infrastructure, and future growth projections. Initially, organizations must evaluate current network capacity, quality requirements, and participant distribution patterns across different locations. Furthermore, detailed assessment of existing communication systems helps identify integration requirements and potential compatibility issues.
Additionally, capacity planning considers peak usage scenarios, concurrent session requirements, and expected participant numbers for various meeting types. Moreover, organizations should evaluate security requirements, compliance obligations, and administrative capabilities necessary for ongoing system management. Therefore, thorough planning ensures successful implementation that meets organizational needs while providing room for future expansion.
Network Infrastructure Considerations
Network infrastructure significantly impacts system performance, requiring careful evaluation and potential upgrades to support communication requirements effectively. Initially, organizations must assess available bandwidth, latency characteristics, and quality of service capabilities across all locations. Furthermore, network segmentation and prioritization mechanisms ensure adequate resources for critical communication traffic.
Additionally, firewall configurations and security policies require careful planning to enable necessary traffic while maintaining organizational security standards. Moreover, redundant network paths and failover mechanisms provide resilience against network failures that could disrupt communication sessions. Consequently, robust network infrastructure serves as the foundation for reliable, high-quality communication systems.
Integration with Existing Systems
Seamless integration with existing communication and business systems enhances productivity while minimizing disruption to established workflows and processes. Initially, organizations should evaluate compatibility between new systems and existing telephony, video, and collaboration platforms. Furthermore, integration planning includes user directory synchronization, authentication systems, and management interface consolidation.
Additionally, API integration enables custom applications and workflows that leverage communication capabilities within existing business processes effectively. Moreover, careful migration planning ensures smooth transition from legacy systems while maintaining service continuity throughout implementation. Therefore, comprehensive integration strategies maximize system value while minimizing implementation complexity and user disruption.
Benefits and Advantages
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Organizations achieve significant cost savings by reducing travel expenses, facility requirements, and time investments associated with traditional meetings. Initially, remote communication eliminates transportation costs, accommodation expenses, and time losses associated with participant travel to meeting locations. Furthermore, reduced facility requirements lower real estate costs and associated overhead expenses for meeting spaces.
Additionally, improved scheduling flexibility enables more frequent meetings and faster decision-making processes that enhance organizational agility significantly. Moreover, recorded sessions provide valuable reference materials that eliminate need for additional meetings and documentation efforts. Therefore, organizations realize substantial return on investment through reduced operational costs and improved productivity.
Enhanced Collaboration
Advanced communication capabilities enable more effective collaboration between distributed teams and external stakeholders across different time zones. Initially, visual communication enhances understanding and engagement compared to audio-only alternatives available through traditional communication methods. Furthermore, screen sharing and document collaboration features enable real-time information sharing and joint problem-solving activities.
Additionally, recorded sessions preserve valuable discussions and decisions for future reference and team members who cannot attend live. Moreover, flexible participation options accommodate different working styles and availability constraints that enhance overall team productivity. Consequently, organizations experience improved collaboration quality and team effectiveness across distributed work environments.
Scalability and Flexibility
Modern systems provide excellent scalability options that accommodate growing organizational needs and changing communication requirements over time. Initially, software-based solutions enable capacity expansion without significant hardware investments or infrastructure modifications. Furthermore, cloud-based implementations provide virtually unlimited scalability with pay-as-needed pricing models that optimize costs.
Additionally, flexible configuration options enable organizations to adapt system capabilities to specific meeting requirements and participant needs. Moreover, integration capabilities allow organizations to enhance functionality by connecting additional systems and services as requirements evolve. Therefore, scalable solutions provide long-term value while adapting to changing organizational needs and technological advancement.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Network Performance Issues
Network-related problems represent common challenges that can significantly impact communication quality and participant experience during sessions. Initially, insufficient bandwidth causes video quality degradation, audio delays, and connection stability problems that disrupt effective communication. Furthermore, network latency creates timing issues that interfere with natural conversation flow and participant interaction.
Additionally, packet loss results in missing audio segments, video artifacts, and synchronization problems that degrade overall session quality. Moreover, network congestion during peak usage periods can overwhelm available resources and cause widespread quality issues. Therefore, organizations must implement comprehensive network monitoring and management strategies to maintain consistent communication quality.
Security Considerations
Security challenges require careful attention to protect sensitive communication content and prevent unauthorized access to organizational information systems. Initially, encryption protocols protect multimedia streams during transmission across potentially insecure network infrastructure between different locations. Furthermore, authentication mechanisms ensure only authorized participants can access communication sessions and associated resources.
Additionally, firewall configurations must balance security requirements with necessary communication traffic flows for optimal system functionality. Moreover, endpoint security measures protect against malware and unauthorized access attempts that could compromise session integrity. Consequently, comprehensive security strategies address multiple threat vectors while maintaining usability and performance standards.
User Adoption and Training
User acceptance and effective utilization represent critical success factors that determine overall system value and organizational benefits. Initially, comprehensive training programs ensure participants understand system capabilities and can utilize advanced features effectively during meetings. Furthermore, ongoing support resources help users overcome technical challenges and maximize system benefits.
Additionally, change management strategies address resistance to new technologies and communication processes that may disrupt established workflows. Moreover, user feedback mechanisms enable continuous improvement and customization that enhance system usability and satisfaction levels. Therefore, successful implementation requires equal attention to technical capabilities and user experience considerations.
Future Trends and Developments
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI technologies promise significant enhancements to communication systems through intelligent automation and advanced processing capabilities that improve user experience. Initially, machine learning algorithms will optimize bandwidth allocation and quality parameters automatically based on real-time conditions and usage patterns. Furthermore, AI-powered features will provide automatic transcription, translation, and meeting summarization capabilities.
Additionally, intelligent speaker identification and activity detection will enable more sophisticated meeting management and participant engagement tracking. Moreover, predictive analytics will help organizations optimize system resources and anticipate capacity requirements based on usage patterns. Consequently, AI integration will transform communication systems into intelligent platforms that enhance productivity and user experience significantly.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud computing continues driving system evolution toward more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions that eliminate traditional infrastructure constraints. Initially, cloud-based implementations reduce capital investments while providing access to advanced capabilities previously available only through expensive hardware. Furthermore, global cloud infrastructure enables consistent performance and availability across distributed organizational locations.
Additionally, cloud providers offer specialized communication services that integrate seamlessly with existing business applications and workflows. Moreover, automatic updates and maintenance reduce administrative overhead while ensuring access to latest features and security improvements. Therefore, cloud adoption accelerates as organizations seek modern, flexible solutions that adapt to changing requirements.
Enhanced Security Features
Evolving security threats drive continuous improvement in protection mechanisms and encryption technologies that safeguard organizational communication content. Initially, advanced encryption protocols provide stronger protection against increasingly sophisticated attack methods and unauthorized access attempts. Furthermore, zero-trust security models ensure comprehensive verification and monitoring of all system access and activities.
Additionally, biometric authentication and behavioral analysis enhance user verification while simplifying access procedures for legitimate participants. Moreover, blockchain technologies may provide immutable audit trails and enhanced security for critical communication sessions. Consequently, security enhancements continue evolving to address emerging threats while maintaining system usability and performance standards.
Final Verdict
Multipoint control units represent essential infrastructure components that enable modern organizations to conduct effective communication and collaboration across distributed environments. Moreover, these systems provide comprehensive capabilities that enhance productivity while reducing costs associated with traditional meeting approaches. Additionally, continued technological advancement promises even greater capabilities and benefits for organizations embracing modern communication solutions.
Furthermore, successful implementation requires careful planning, adequate infrastructure, and comprehensive user training to maximize system value and organizational benefits. Subsequently, organizations that invest in these technologies position themselves for improved collaboration, enhanced productivity, and competitive advantages in distributed work environments. Therefore, understanding and implementing these systems becomes increasingly important for organizational success in modern business environments.